Can a Bad Tooth Cause Swollen Glands?
Yes, a bad tooth can cause swollen glands. When a tooth is infected or abscessed, the infection can spread to nearby lymph glands (commonly referred to as “glands”) in the neck and under the jaw. This swelling occurs as part of the body’s immune response to the infection. If you experience swollen glands along with tooth pain or other dental issues, it’s important to consult a dentist promptly to address the infection and prevent further complications.
Have you ever wondered why your glands might swell up when you’re battling a toothache?
It’s not just happenstance. When you have a bad tooth, the infection from the tooth can spread beyond just the oral cavity and start affecting nearby structures, including your glands. This can lead to swollen lymph nodes, which are fundamentally your body’s way of trying to fight the infection.
It’s important to understand the signs and how swiftly complications can arise. What’s more intriguing is how this seemingly localized issue can have broader implications for your overall health. Let’s explore how this happens and what you can do about it.
Tooth Infections
Understanding tooth infections, it’s vital to recognize that they stem from bacterial growth within the dental pulp, the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels.
When these bacteria invade and multiply, they can cause an infection that may lead to the formation of a tooth abscess, a pocket of pus that develops in different regions of the tooth as a defense mechanism against the infection.
The spread of infection from the tooth abscess can cause significant implications for surrounding tissues, including the lymph nodes. These nodes act as filters for foreign particles and are pivotal in activating your immune response. When a tooth infection becomes severe, the bacteria or their byproducts can escape into the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining lymph fluid from tissues, including those around the infected tooth.
This migration can result in inflammation and swelling of the lymph nodes, often observed in the neck or jaw regions. It’s imperative to understand the pathways of infection spread and the role of the lymphatic system in order to grasp how dental health impacts overall physiological wellness.
Infections that aren’t promptly or properly treated can lead to more severe health issues, emphasizing the importance of timely dental intervention.
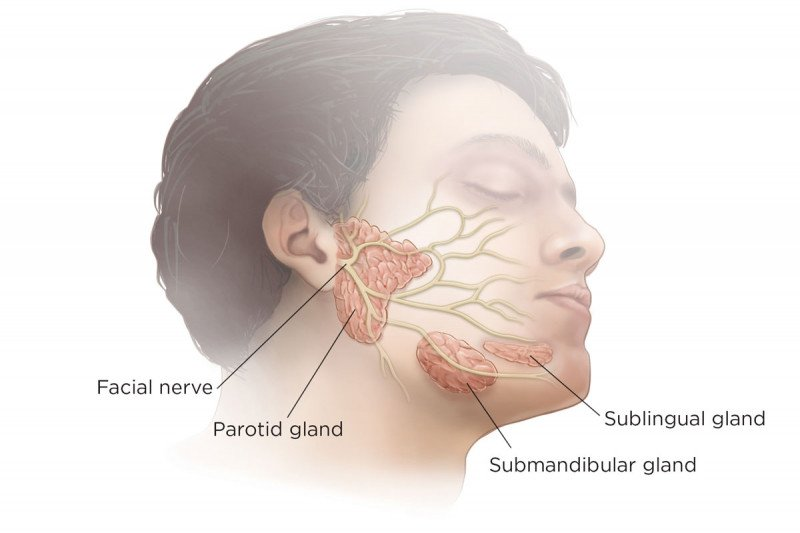
Symptoms and Signs Swollen Glands
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of a tooth infection is vital to managing and preventing further spread to areas like the lymph nodes. Two primary indicators to be aware of are tooth pain and swollen glands.
Tooth pain, often sharp and pulsating, can indicate the presence of an infection. It typically originates from the affected tooth and might intensify when you bite down or consume hot or cold beverages. This discomfort results from the inflammation of the tooth’s nerve due to bacterial invasion that breaches the tooth’s protective enamel and dentin layers, reaching the pulp.
Swollen glands, another significant symptom, are typically located in the neck or jaw areas. These glands, or lymph nodes, swell as part of the body’s immune response to infection. They work to filter out and trap bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. When they detect the bacteria from an infected tooth, they increase in size, a process known as lymphadenopathy. This swelling can be tender or painful upon palpation and might be accompanied by general feelings of malaise or fever as the body fights the infection.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a dental professional promptly.
How Infections Spread

Infections from a bad tooth can rapidly spread to adjacent tissues, including the jawbone and soft tissues of the oral cavity, potentially reaching systemic circulation. The progression of this infection depends significantly on the lymph node connection.
As bacteria proliferate at the infection site, they can infiltrate the lymphatic system, which serves as a conduit for transporting fluids and immune cells throughout your body. This system’s extensive network allows for quick dissemination of infectious agents, leading to swollen lymph nodes, commonly experienced as tender lumps near your jaw and neck.
The mechanism of infection spread is facilitated by the lymphatic drainage from the oral region connecting directly to the cervical lymph nodes. These nodes act as filters, attempting to clear the bacteria before they can spread further. However, if the infection is severe or the immune response is compromised, these nodes swell, signaling an ongoing battle against the infection.
This lymphatic involvement underscores the significant nature of addressing dental infections promptly to prevent their escalation into more severe systemic conditions. Understanding this pathway illustrates why maintaining oral hygiene is important, not just for dental health but for general well-being.
Ignoring a dental issue can lead to widespread implications due to this swift and efficient infection spread mechanism.
Diagnosing Dental Issues
To accurately identify dental problems that might be causing your swollen glands, you’ll need to recognize the signs of underlying oral disease. This involves observing symptoms such as:
- Persistent toothache
- Gum redness
- Unusual swelling around the jaw or neck area
A thorough examination by a dental professional, using tools such as X-rays or intraoral cameras, is essential to pinpoint the specific issues affecting your oral health.
Identifying Dental Problems
When diagnosing dental issues, evaluating symptoms like pain, swelling, or discomfort in the teeth and gums is vital. It is necessary to determine whether these symptoms stem from tooth decay or other dental pathologies. Swollen glands, often a reactive sign, can indicate an infection sourced from a bad tooth.
Identifying the specific dental problem responsible is crucial in providing effective treatment and preventing further complications.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of common indicators and potential dental issues they might signify:
| Symptom | Possible Dental Issue | Associated Problems |
|---|---|---|
| Persistent Pain | Tooth Decay | Infection, Swollen Glands |
| Swelling | Gum Disease | Infection, Tooth Loss |
| Discomfort | Cracked or Fractured Teeth | Nerve Damage, Infection |
| Bad Breath | Bacterial Buildup | Decay, Gum Disease |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Exposed Dental Pulp | Decay, Possible Root Infection |
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with your dentist promptly. Delaying diagnosis and treatment can lead to more severe health issues, including the spread of infection to other parts of your body. A timely visit to the dentist can mitigate these risks, ensuring your dental and overall health are preserved.
Signs of Oral Disease
Recognizing the signs of oral disease requires a keen understanding of various symptoms that might indicate underlying dental issues. You must be vigilant about your oral health, as early detection plays a vital role in preventing more severe conditions. Common indicators include persistent bad breath, sensitive teeth, and swollen, bleeding gums. These symptoms may suggest gingivitis or, more seriously, periodontal disease.
Moreover, discomfort or pain when chewing can signal decay or an abscess, which, if left untreated, could lead to more significant infection or tooth loss.
It’s also important to watch for changes in the color or texture of your gums, teeth, or tongue, as these can reveal signs of disease not immediately obvious to the untrained eye.
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw area are particularly notable. They often enlarge as a response to infection or inflammation in the mouth. This enlargement of the lymph nodes is a crucial sign that your body is fighting an infection, possibly linked to a dental issue.
If you notice such changes, it’s essential to seek professional dental care promptly to address the root cause and mitigate any potential complications related to your oral health.
Treatment Options swollen glands
Addressing a bad tooth that causes swollen glands typically involves both dental intervention and medical treatment to alleviate infection and inflammation. When you’re dealing with swollen glands due to a dental issue, the primary focus is to eliminate the source of infection, which might include procedures such as tooth extraction.
If the affected tooth is severely decayed or abscessed, extracting it can prevent the spread of infection that contributes to the swelling of glands.
Post-extraction, your dentist will likely prescribe antibiotics to combat any residual bacterial presence. It’s essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed to guarantee all infection is eradicated, reducing the risk of further swelling or complications.
Additionally, your dentist may recommend saline mouth rinses or specific oral hygiene practices to support healing and prevent new infections.
For pain management and to reduce inflammation in the swollen glands, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen can be effective. These should be used according to the recommended dosages and it’s prudent to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Managing pain and inflammation not only makes you more comfortable but also facilitates a quicker recovery by reducing stress on your immune system.
Preventing Further Complications
To mitigate the risk of swollen glands due to dental issues, it’s important that you seek early dental intervention when symptoms first appear.
Regular hygiene practices, including thorough brushing and flossing, play a significant role in preventing the escalation of infections that can lead to complications.
Addressing dental health concerns promptly and maintaining a consistent oral care routine are key strategies in avoiding severe health issues.
Early Dental Intervention
Initiating dental intervention early can greatly reduce the risk of further complications such as swollen glands caused by a bad tooth. Addressing dental issues promptly isn’t just about alleviating immediate pain—it’s essential in preventing the escalation of infection, which can lead to more serious health problems including the swelling of lymph nodes.
Efficient management of dental emergencies is a cornerstone of maintaining long-term oral health and overall wellness. Here are key strategies to ensure effective early dental intervention:
- Prompt Diagnosis: Seek immediate consultation when experiencing unusual oral discomfort. Timely diagnosis using advanced imaging techniques can pinpoint the exact issues, from decay to deeper infections, preventing the spread and reducing complications.
- Proactive Treatment Plans: Don’t wait for the pain to become unbearable. Early treatment plans, which could range from fillings to root canals, are vital in arresting the progression of tooth decay and infection.
- Regular Professional Assessments: Engaging in routine dental check-ups allows for early detection and management of potential dental issues before they evolve into emergencies.
Regular Hygiene Practices
How can regular dental hygiene practices help prevent further complications from a bad tooth? By adopting meticulous brushing habits and flossing techniques, you can greatly minimize the risk of infections that lead to swollen glands. It’s essential to remove food particles and bacterial plaque that accumulate around a bad tooth, as these can worsen the condition.
Proper flossing techniques, in particular, are vital. They ensure that the spaces between your teeth, which are often overlooked, are clean and free from debris. This not only prevents plaque buildup but also decreases the chances of gum disease, which is often a precursor to more severe dental issues.
Incorporating mouthwash as part of your dental routine can also offer additional plaque prevention benefits. Antiseptic mouthwashes reduce bacterial load in the mouth, providing a secondary layer of protection against infection.
To visualize the impact of these practices, consider the following table detailing key aspects of dental hygiene:
| Technique | Benefit | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Brushing | Removes plaque, reduces tartar buildup | Twice daily |
| Flossing | Cleans hard-to-reach areas, reduces gum disease risk | At least once daily |
| Mouthwash | Decreases bacterial load, aids in plaque prevention | After brushing and flossing |
Can Swollen Glands Indicate Issues Other Than Tooth Infections?
Yes, swollen glands can signal various conditions, such as glandular fever or allergies, and could result from medication interactions. It’s important to take these possibilities into account to avoid misdiagnosis. Consult a healthcare professional for clarity.
Are There Natural Remedies for Reducing Gland Swelling?
Yes, you can try herbal remedies and dietary changes to reduce gland swelling. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like ginger and turmeric, and using herbal teas such as chamomile, may help alleviate your symptoms.
How Quickly Do Symptoms Appear After a Tooth Infection Develops?
Symptoms can appear soon after infection, usually within days. Early detection and medical intervention are essential for effective pain management and accelerating the healing process, minimizing complications associated with the infected tooth.
Can Children Experience Swollen Glands Due to Tooth Decay?
Yes, children can experience swollen glands due to tooth decay, especially if their diet lacks nutrients and oral hygiene is neglected. These factors can exacerbate infections, leading to noticeable swelling in the lymph nodes.
Is It Safe to Exercise With a Tooth Infection and Swollen Glands?
You should consult a healthcare professional before exercising with a tooth infection and swollen glands, as it could worsen your condition. Prioritizing dental care and exercise safety is important for maintaining oral health.
Conclusion
Finally, you must address tooth infections promptly to prevent the spread of bacteria to surrounding tissues, including your lymph nodes.
Neglecting a bad tooth can lead to swollen glands, signaling an immune response. Professional dental intervention is essential to diagnose the specific issue and implement the appropriate treatment.
By doing so, you’ll mitigate the risk of further complications and support your overall health. Remember, proactive dental care is key to preventing such systemic effects.